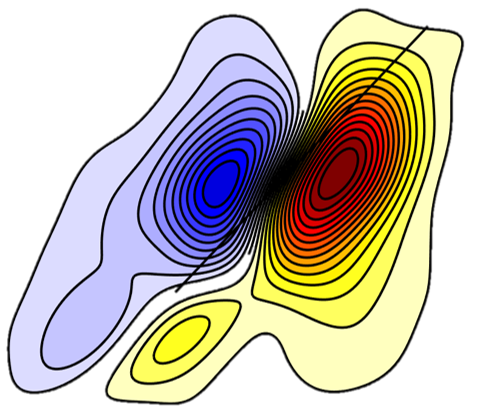
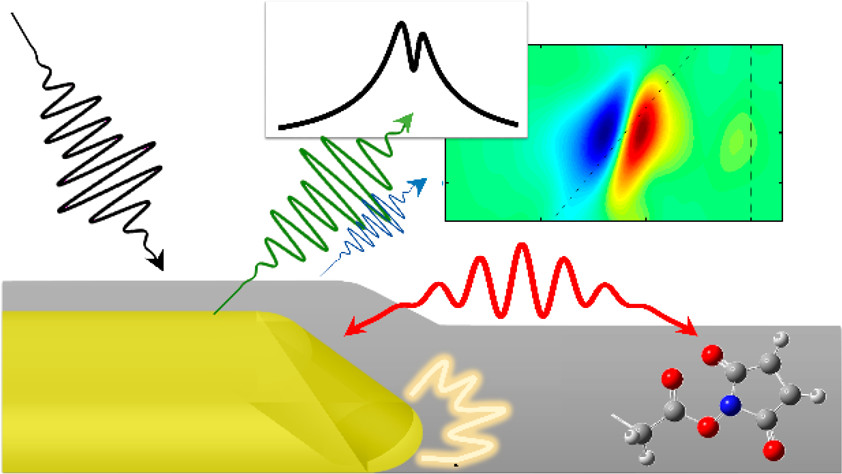
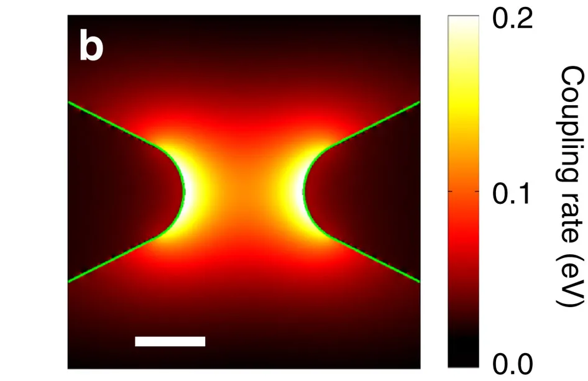
Infrared gold antennas localize enhanced near fields close to the metal surface, when excited at the frequency of their plasmon resonance, and amplify vibrational signals from the nearby molecules. We study the dependence of the signal enhancement on the thickness of a polymer film containing vibrational chromophores, deposited on the antenna array, using linear (FTIR) and third-order femtosecond vibrational spectroscopy (transient absorption and 2DIR). Our results show that for a film thickness beyond only a few nanometers the near-field interaction is not sufficient to account for the magnitude of the observed signal, which nevertheless has a clear Fano line shape, suggesting a radiative origin of the molecule–plasmon interaction. The mutual radiative damping of plasmonic and molecular transitions leads to the spectroscopic signal of a molecular vibrational excitation to be enhanced by up to a factor of 50 in the case of linear spectroscopy and over 2000 in the case of third-order spectroscopy. A qualitative explanation for the observed effect is given by the extended coupled oscillators model, which takes into account both near-field and radiative interactions between the plasmonic and molecular transitions.
Authors: Andrey Gandman, Robert T Mackin, Bar Cohn, Igor V Rubtsov, Lev Chuntonov