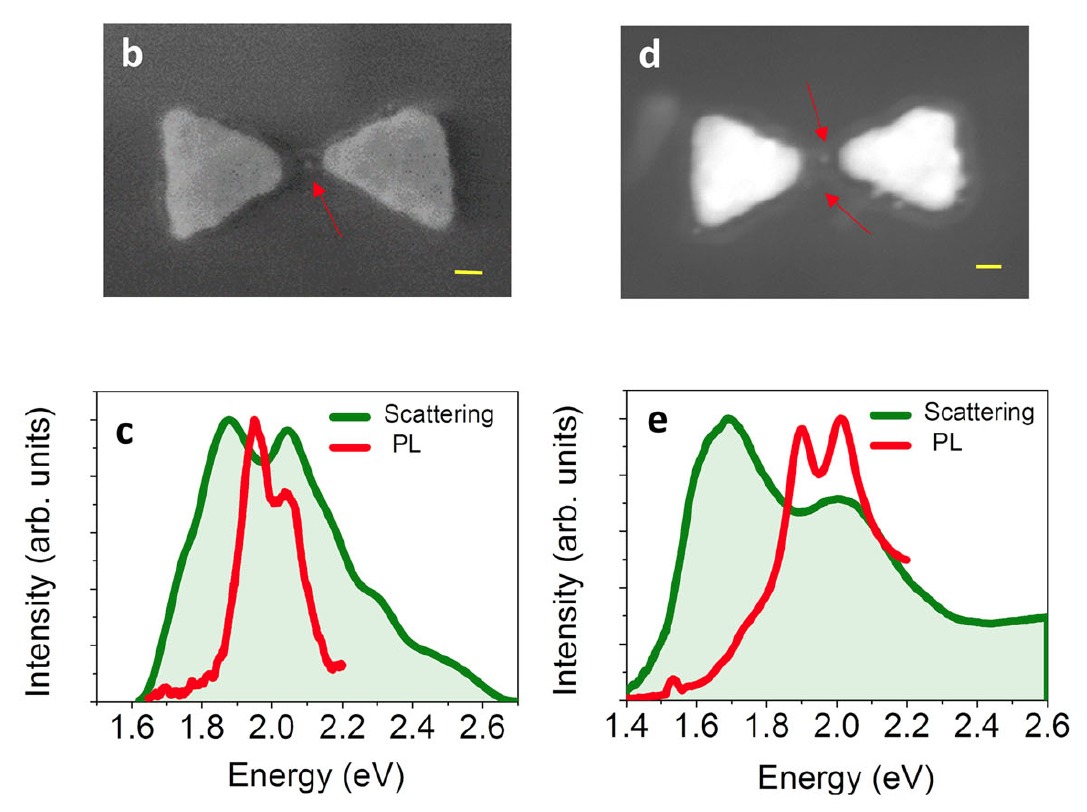
Plasmonic cavities can confine electromagnetic radiation to deep sub-wavelength regimes. This facilitates strong coupling phenomena to be observed at the limit of individual quantum emitters. Here, we report an extensive set of measurements of plasmonic cavities hosting one to a few semiconductor quantum dots. Scattering spectra show Rabi splitting, demonstrating that these devices are close to the strong coupling regime. Using Hanbury Brown and Twiss interferometry, we observe non-classical emission, allowing us to directly determine the number of emitters in each device. Surprising features in photoluminescence spectra point to the contribution of multiple excited states. Using model simulations based on an extended Jaynes-Cummings Hamiltonian, we find that the involvement of a dark state of the quantum dots explains the experimental findings. The coupling of quantum emitters to plasmonic cavities thus exposes complex relaxation pathways and emerges as an unconventional means to control dynamics of quantum states.
Satyendra Nath Gupta, Ora Bitton, Tomas Neuman, Ruben Esteban, Lev Chuntonov, Javier Aizpurua & Gilad Haran